General introduction to HAN's Fiber Concrete Spacer
HAN concrete spacer is a product cast in concrete, contributing to positioning the steel layer in reinforced concrete structures. The main function of HAN concrete support is to create a fixed distance between the steel layer and the formwork so that when pouring concrete, it creates an outer concrete layer with the function of protecting the reinforced concrete structure inside from the corrosive effects of the external environment such as: oxidation, rust or corrosion of the steel layer causing destruction of the structure and making the construction unsafe.
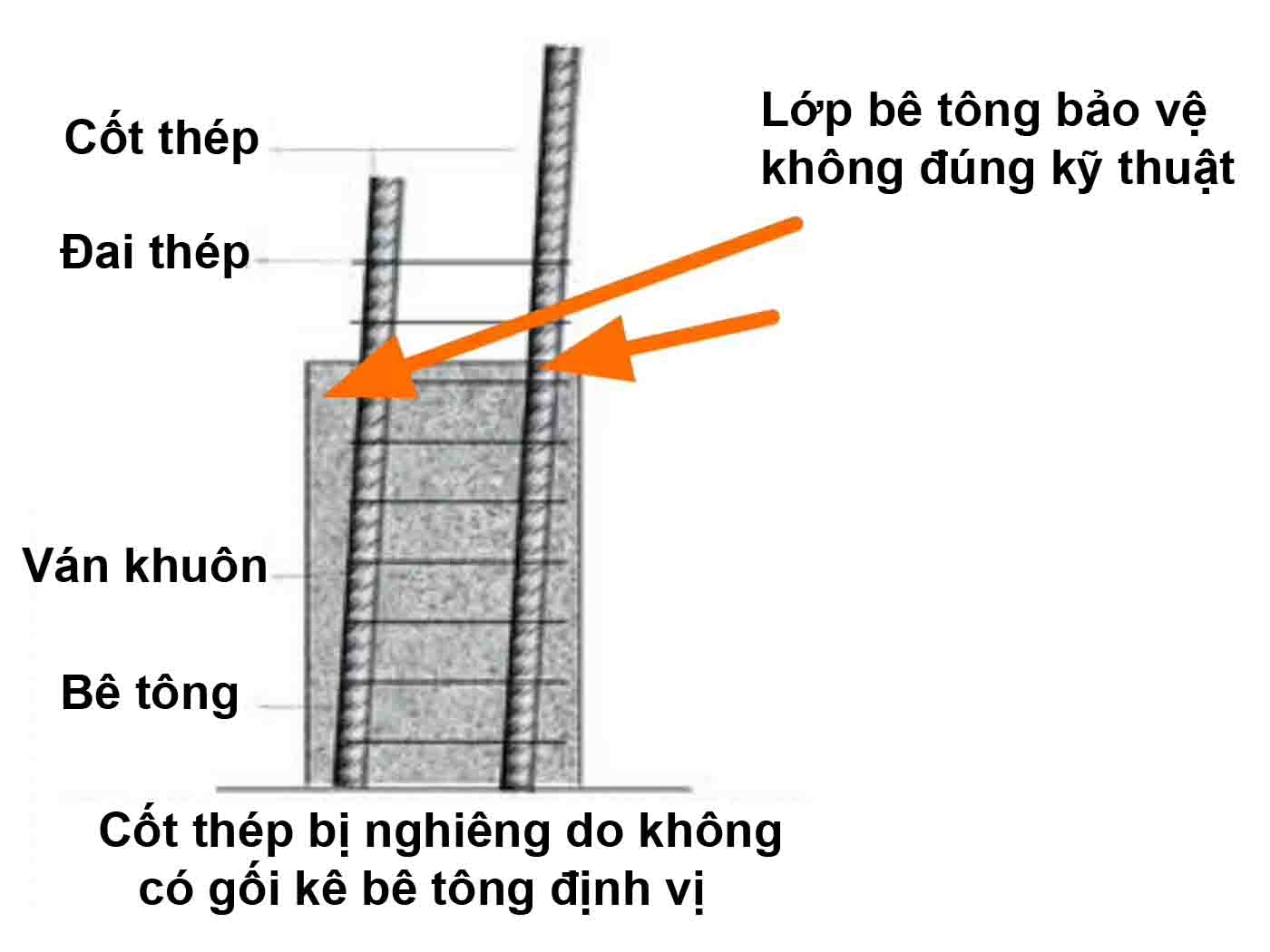
Concrete spacer help form a protective concrete layer properly
will help the steel layer to be positioned correctly
It can be said that concrete spacer contribute to creating a protective concrete layer to help reinforced concrete structures avoid the corrosive effects of the external environment.
Therefore, the quality of concrete spacer must comply with the requirements of the protective concrete layer according to current construction standards.
HAN concrete spacer are one of the concrete structure products manufactured and supplied by HAN Joint Stock Company. HAN concrete spacer are products in the structural category within the HAN product ecosystem solution spectrum
Why should we only use HAN's Fiber concrete spacer and not plastic spacer, iron chairs, or Poor quality concrete block?
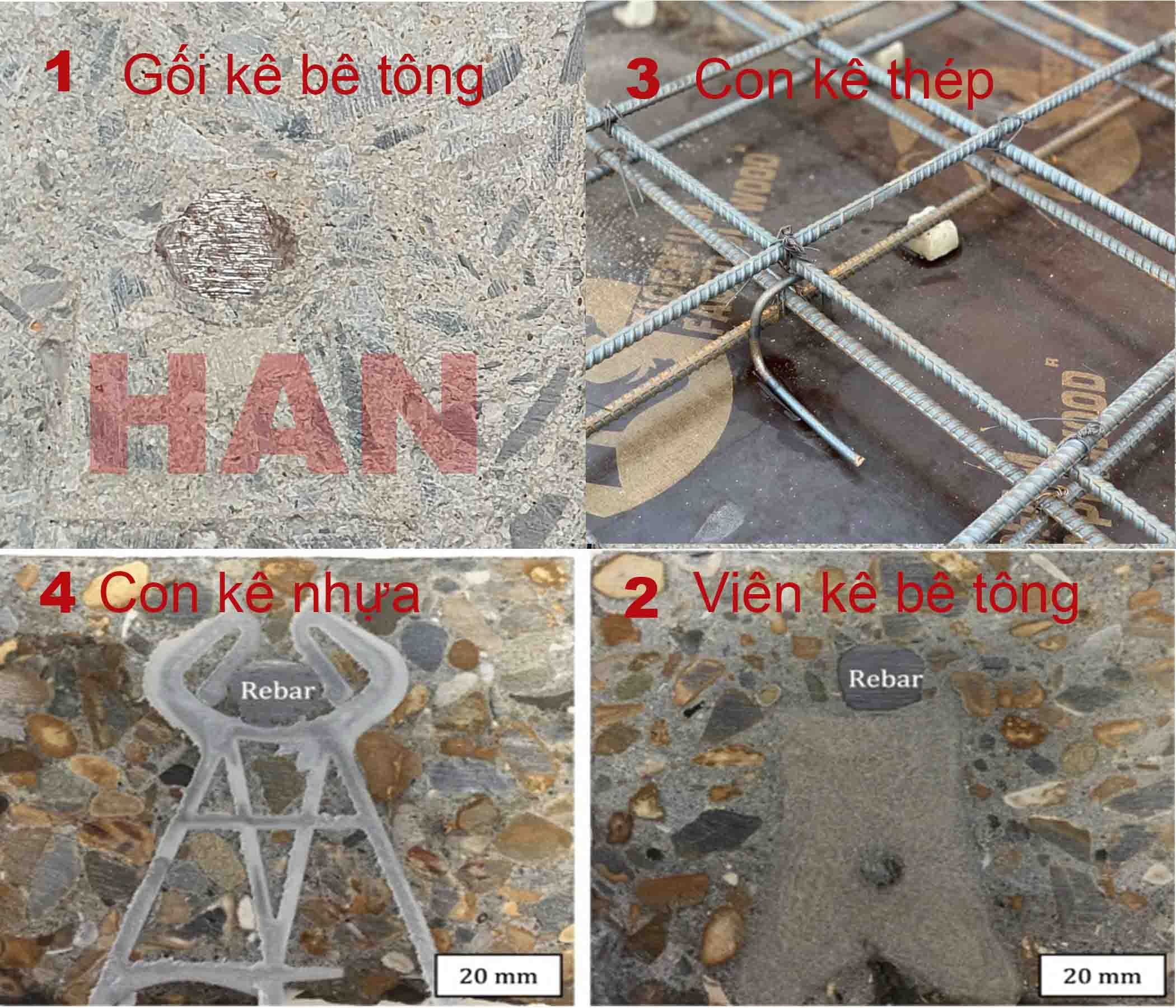

Illustrative image link:
1. HAN Fiber concrete spacer
2. Poor Quality Concrete block
3. Steel bar chairs
4. Plastic concrete spacer
Through the image above, 1. HAN Fiber concrete spacer is homogenous, identical to the concrete layer, has more advantages in:
- Good rust resistance than steel bar chairs,
- More similar elasticity than plastic concrete spacer
- Better waterproofing than plastic concrete spacer, steel bar chairs
- Higher load capacity than other poor quality concrete block.
How to identify HAN 's Fiber concrete spacer with poor quality block spacers, motar spacers, substandard concrete spacers. motar blocks?
Spacer, Low quality concrete spacer, substandard concrete spacer, motar blocks or motar spacers is a common term in the construction industry used to refer to an object of any shape to support steel bars such as: granite block, cement mortar block, brick, etc. Motar Spacer, motar block, poor quality concrete spacer, substandard concrete spacers contain general meanings that do not specify technical features and are produced by hand, with inconsistent quality.

HAN Fiber concrete spacer is a high-tech concrete product manufactured by modern technology process in accordance with current construction standards.
| No | Distinguishing criteria | spacer, motar spacer, substandard spacer, poor concrete spacers | HAN Fiber concrete spacers |
| 1 | Concrete grade |
Unclear or very low |
Concrete grade standard, ≥M600 |
| 2 | Dimension |
Not correct |
Tolerance within allowable range |
| 3 | Design shape |
Basic, not optimal |
Diverse designs for every need |
| 4 | Production technology |
Handcrafted, poor quality |
Machinery, high standard quality |
| 5 | Raw Material |
Substandard, no or very little reinforcing fibers |
Standard, with effective participation of reinforcing fibers |
| 6 | Breaking Load |
poor load capacity |
High load capacity |
| 7 | Economic efficiency |
Low |
High |
Classification of HAN's Fiber concrete spacers:
| No | Classification criteria | Types of HAN's Fiber concrete spacer |
| 1 | Intended use |
- Fiber Concrete Spacer for foundations - Fiber Concrete Spacer for beams - Fiber Concrete Spacer for columns - Fiber Concrete Spacer for floors - Fiber Concrete Spacer for precast structures - Fiber Concrete Spacer for bridge girders - Fiber Concrete Spacer for bored piles |
| 2 | Design style |
- Single size Fiber concrete Spacer - Multi size Fiber concrete Spacer - Fiber concrete Spacer with tie wire - Round Fiber concrete Spacer - Bar Fiber concrete Spacer |
| 3 | Raw Material |
- Fiber concrete spacer |
| 4 | Concrete Grade |
- Concrete spacer standard - High quality Fiber Concrete spacer |
| 5 | Breaking Load |
- standard concrete spacer - Heavy Duty concrete spacer |
| 6 | Technical Standard |
- Concrete Spacer for civil construction - Concrete Spacer for industrial construction |
Identifying characteristics of each type of HAN concrete spacer:
| No | Characteristic | Single size Fiber concrete Spacer |
Multi size Fiber concrete Spacer | Fiber concrete Spacer with tie wire | Round Fiber concrete Spacer |
Bar Fiber concrete Spacer |
| 1 | Design | only 1 size each design | ≥2 size each design | regular 1 size each design | almost 1 size each design | only 1 size each design |
| 2 | Shape | Trapezoidal, A-shaped, U-shaped, ... with a hollow hole in the middle, flat or concave base | Flower, cubic, hollow in the middle, concave or flat base | Square or round cylinder, with attached tie wire | Circular with a hole in the center. Flat or wavy surface | Long, flat or curved bar, flat base |
| 3 | Cover size | 20 … 150 mm | 20 … 150 mm |
20 … 150 mm |
20 … 150 mm |
20 … 50 mm |
| 4 | Use priority for | Foundation, basement, beam, floor, column, beam, floor, wall, roof, concrete structure |
Foundation, basement, beam, floor, column, beam, floor, wall, roof, concrete structure |
Foundation, basement, beam, floor, column, beam, floor, wall, roof, concrete structure |
Foundation, basement, beam, floor, column, beam, floor, wall, roof, concrete structure |
Beams, floors, walls, concrete structures |
| 5 | Color | Natural concrete gray |
Natural concrete gray |
Natural concrete gray |
Natural concrete gray |
Natural concrete gray |
| 6 | Production technology | Machinery, concrete casting | Machinery, concrete casting | Machinery, concrete casting | Machinery, concrete casting | Machinery, concrete casting |
| 7 | Raw Material | Qualified | Qualified | Qualified |
Qualified |
Qualified |
| 8 | Breaking load | Rather | Rather | Good | Good | Good |
| 9 | Anti-rollover | Rather | Rather | Good | Good | Good |
| 10 | Packing | Plastic bag. carton box | Plastic bag. carton box | Plastic bag. carton box | Plastic bag. carton box | Plastic bag. carton box |
Materials for manufacturing HAN concrete spacer
Materials for manufacturing HAN concrete spacers include: sand, cement, stone, water, additives, reinforcing fibers, ... meeting current construction standards
HAN concrete spacer manufacturing technology: HAN's Fiber concrete spacers are manufactured using concrete casting technology. Concrete products are cast for precise dimensions, low tolerances
How to choose and use HAN's concrete spacers to achieve high economic and technical efficiency
| No | Criteria | Should | Shouldn't |
| 1 | Quantitative use of science - Economics | Should use equal to or higher than the recommended usage of HAN and need to consider construction practice to adjust accordingly. | Do not use less than the recommended dosage by HAN although the Breaking load capacity of the concrete spacer is very good. |
| 2 | Design the right product |
You should choose the design that is suitable for construction requirements and has a high safety factor to maximize the products effectiveness. |
Do not, for convenience, get into the habit of using one design for many construction needs, even if they are the same size, as this will reduce the efficiency of the product. |
| 3 | Optimum concrete grade |
You should choose the type with standard concrete grade, suitable for the requirements of reinforced concrete structures. |
You should not choose a type that is too high or a type that is specially designed for normal use only, which will be wasteful, inappropriate, and unnecessary. |
| 4 | Exact size according to construction requirements | You should know all the types of the same size that HAN is providing, from there choose the appropriate type. |
Don't buy out of habit or buy based on recent history because HAN has many better versions worth experiencing |
| 5 | Economic efficiency | Need to pay attention to the final economic efficiency | Don't just look at the price of each type of spacer to choose. |
| 6 | Optimal quantity | You should have a suitable shopping plan and buy sparingly (buying a little more than you need to have spares and having cheap shopping costs is essential). |
Do not buy retail, only buy when needed or do not predict the quantity to buy without knowing the specific construction requirements and usage standards. |
| 7 | Person in charge | The decision maker must have the knowledge and experience to make appropriate decisions. | Do not just hand over purchasing to warehouse staff or supply staff without fully understanding the technical features of the product. |
| 8 | Suitable packaging |
Should buy in bulk at once if the project has many related items, use according to progress, should choose the bagged type, the price will be cheaper and convenient for transportation, storage, preservation, and construction. If the quantity is small, you can consider combining combo packages if available |
Do not buy small amounts, buy retail, or buy in batches as this will result in additional purchasing and shipping costs. |
| 9 | HAN brand awareness |
You should carefully observe HAN information on the packaging, quality, and specifications. Buy from distributors or from HAN's factory. |
Do not buy products that do not have clear manufacturer information on the packaging or are not from HAN distributors or factories. |
Methods of transportation and storage of HAN concrete spacers
Notes when tran sporting HAN concrete spacers:
- Do not drag the packaging on the ground, avoid throwing it from above if packaged
- When tran sporting concrete spacer bags or concrete spacer boxes, use a flat-floor truck
- Heavy bags, suitable products are placed below, the steel concrete spacers on the upper floor (note: CSS050U, CSS070U, CSS090U, CSS110U, ...) are placed on top, do not stack too high.
Notes when storing HAN concrete spacers:
- Should be placed on a cool, dry floor, avoid direct contact with soil, mud, moisture, mold
- If packaged in bags, it can be left outside for 1-3 months
- If packaged in boxes, it must be placed on a pallet, not exposed to water or high humidity
Quality standards of HAN concrete spacers
HAN concrete support pillows fully meet the following standards:
Standard TCXDVN 356: 2005 "Concrete and Reinforced Concrete Structures - Design Standards"
Standard TCVN 4116: 1985 "Concrete and Reinforced Concrete Structures for Hydraulic Works - Design Standards"
Standard TCVN 9139: 2012 "Irrigation Works - Concrete and Reinforced Concrete Structures in Coastal Areas - Technical Requirements"
Standard TCVN 9346: 2012 "Concrete and Reinforced Concrete Structures - Requirements for Protection against Corrosion in Marine Environments"
Standard TCVN 5574: 2018 "Design of Concrete and Reinforced Concrete Structures"
Standard BS 7973-1: 2001 (British Standard) Spacers and chairs for steel reinforcement and their specification - Product performance requirements
Standard BS 8110 – 1997 (British Standard) “Concrete and reinforced concrete structures”
Advantages of HAN concrete spacers compared to other solutions: plastic spacer, steel bar chairs
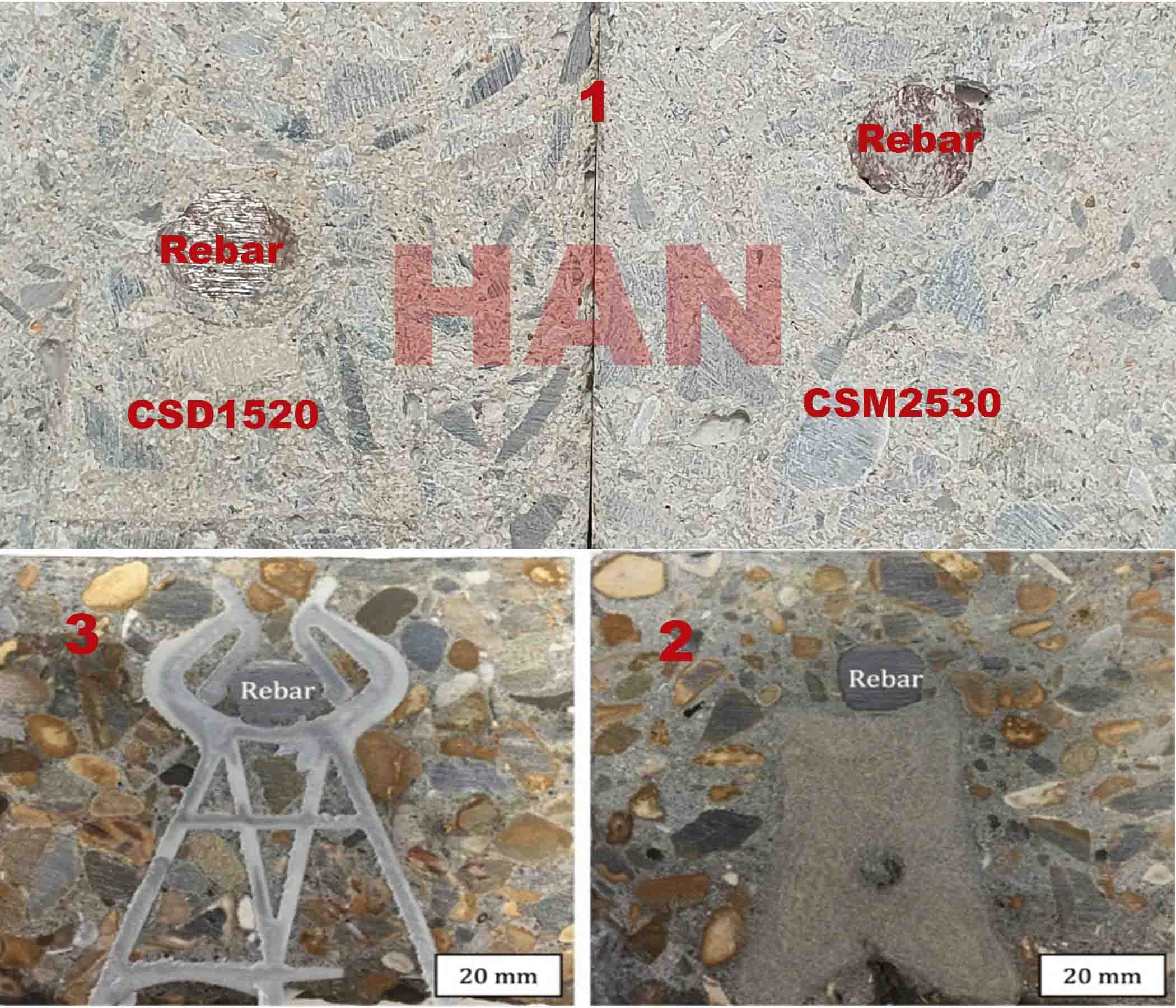
Illustration of the advantages of HAN concrete spacers compared to plastic spacer:
Same materials, homogeneous, same origin,good load-bearing design, good waterproofing,....
Answer: A concrete spacer is an accessory used to maintain the precise spacing between reinforcement bars and the outer concrete surface, ensuring the concrete cover meets the required standards.
Explanation: Concrete spacers play a crucial role in protecting reinforcement steel from corrosion, enhancing fire resistance, and ensuring structural durability. Without them, reinforcement bars may come into direct contact with the environment, which can significantly reduce the service life of the structure.
Optimization: Choose high-quality concrete spacers that meet standards such as BS 7973-1 or DIN 1045 to ensure safety and efficiency.
Answer: Common types of concrete spacers include:
● Single-size concrete spacers.
● Multi-size concrete spacers.
● Circular and bar-shaped spacers.
● Concrete spacers with zinc-coated wires.
● Plastic and steel spacers.
Explanation: Each type of spacer has specific applications suitable for different structural components such as slabs, columns, walls, or beams.
Optimization: Determine the appropriate type of spacer based on the design requirements and the load of the structure.
Answer: Common types of concrete spacers include:
● Single-size concrete spacers.
● Multi-size concrete spacers.
● Circular and bar-shaped spacers.
● Concrete spacers with zinc-coated wires.
● Plastic and steel spacers.
Explanation: Each type of spacer has specific applications suitable for different structural components such as slabs, columns, walls, or beams.
Optimization: Determine the appropriate type of spacer based on the design requirements and the load of the structure
Answer: Yes, especially in the Interfacial Transition Zone (ITZ) between the spacer and the concrete.
Explanation: Studies have shown that the interface area typically has higher porosity and microcracks, which can increase chloride permeability and reduce durability. However, improving the spacer's surface texture can address this issue.
Optimization: Choose spacers with treated rough surfaces or fiber-reinforced concrete spacers to enhance the bond strength
Answer: The quality of concrete spacers can be tested through experiments such as:
● Compression strength testing.
● Water permeability evaluation.
● Chloride diffusion resistance testing.
Explanation: Standards like ASTM C1202 or RCP tests help assess the spacer's effectiveness in protecting against corrosive environments.
Optimization: Conduct regular testing before use in construction
Answer: Depending on the structural component, the recommended concrete cover thickness values are as follows:
|
Component Type |
Concrete Cover Thickness (mm) |
Notes |
|
Pile footing (Footing) |
50 |
Ensures protection against moisture and corrosion from soil or groundwater. |
|
Raft foundation |
Top: 50 |
Applies to top reinforcement. |
|
|
Bottom: 75 |
Thicker cover to resist harsh corrosive environments from soil. |
|
Column |
40 |
Common for indoor columns or general load-bearing columns. |
|
Shear wall |
25 |
Applies to load-bearing walls and wind-resistant walls in structures. |
|
Beam |
25 |
Suitable for main reinforcement resisting bending and shear forces in beams. |
|
Slab |
15 |
For typical slabs not directly exposed to corrosive environments. |
|
Flat slab |
20 |
For slabs without beams, providing sufficient protection for main reinforcement. |
|
Staircase |
15 |
Meets standard load requirements and resists wear during usage. |
|
Retaining wall |
20 (inner side) |
The side in direct contact with water or soil. |
|
|
25 (outer side) |
The outer side to resist corrosive environments or extreme climate effects. |
Explanation: The concrete cover helps minimize reinforcement corrosion and maintains structural durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Optimization: Use spacers with heights that match the designed concrete cover thickness
Answer: Yes, if they are designed to meet exposure class standards such as X0, XC, XD, and XS.
Explanation: These standards define the durability of spacers in conditions like water immersion, marine environments, or areas with corrosive chemicals.
Optimization: Choose spacers certified by reputable organizations such as ASTM or Euro code 2
Answer: Spacers should be installed evenly with a maximum spacing of 1m or a recommended spacing of 50D (where D is the reinforcement diameter), ensuring they do not shift during concrete pouring.
Explanation: The placement of spacers directly affects the accuracy of the concrete cover and the structural load capacity.
Optimization: Use spacers designed with anti-slip features or secure fastening to reinforcement
Answer: Concrete spacers are generally better for long-term durability, while plastic spacers are lighter and easier to install.
Explanation: Concrete spacers have better bonding with structural concrete, whereas plastic spacers are less affected by chemicals.
Optimization: Choose concrete spacers for large projects or harsh environments
Answer: Optimize costs by selecting the right type of spacer and ensuring quality control.
Explanation: Use multi-size spacers for different components to reduce waste and increase construction efficiency.
Optimization: Calculate the required quantity of spacers based on the design and avoid exceeding the prescribed amount
Answer: Fiber-reinforced concrete spacers have higher durability, better crack resistance, and ensure a stronger bond with the surrounding concrete.
Explanation: The reinforcing fibers enhance compressive strength and minimize the risk of cracking at the spacer-concrete interface.
Optimization: Use fiber-reinforced spacers for high-durability structures or in harsh environments like coastal areas
Answer: They may have a slight effect if the spacers create poor-quality interfaces or cause segregation in the concrete.
Explanation: Studies show that the interface zone between spacers and concrete can have high porosity, which may reduce overall compressive strength.
Optimization: Ensure proper installation of spacers and select products with well-treated surfaces to minimize negative impacts
Answer: Plastic spacers may not bond well with concrete and are prone to shifting during pouring.
Explanation: Plastic lacks natural roughness, increasing the risk of cracks at the interface and reducing load-bearing capacity.
Optimization: Use plastic spacers only for smaller projects or structures with low load requirements
Answer: The size of spacers is selected based on the designed concrete cover thickness.
Explanation: Standards like Eurocode 2 or BS 7973-1 specify the cover thickness for different components (e.g., footings, columns, slabs, walls).
Optimization: Refer to manufacturer specifications and design standards to select the correct size
Answer: No, concrete spacers are designed to become a permanent part of the structure.
Explanation: Reusing spacers can reduce their quality and compromise the structure's durability.
Optimization: Always use new spacers to ensure quality and safety
Answer: Yes, particularly at the interface between the spacer and the concrete.
Explanation: The spacer-concrete interface often has higher water permeability, increasing the risk of chloride ingress or corrosive substance penetration.
Optimization: Use spacers with high chloride resistance or special surface treatments to improve water resistance
Answer: Typically, 4-6 spacers are required per square meter, depending on the structural type and design load.
Explanation: Proper spacing ensures that the reinforcement remains in place during construction and maintains the designed cover thickness.
Optimization: Calculate the specific quantity based on construction drawings or consult the manufacturer
Answer: Yes, inspection is necessary to ensure that spacers remain in place and meet design specifications.
Explanation: Poor pouring practices can cause spacers to shift, compromising the protective cover.
Optimization: Use cameras or non-destructive testing (NDT) equipment for post-pouring inspections.
Answer: Steel spacers are generally unsuitable for corrosive or wet environments.
Explanation: Steel is prone to rust, which can degrade the quality and lifespan of the protective concrete cover.
Optimization: Use concrete or plastic spacers in high-corrosion areas such as coastal environments
Answer: Yes, spacers with high chloride resistance and anti-corrosion properties are necessary.
Explanation: Marine environments have high humidity and salt content, which can quickly corrode reinforcement if the protective cover is inadequate.
Optimization: Choose fiber-reinforced concrete spacers or spacers with special surface treatments for enhanced corrosion resistance
Answer: Yes, concrete spacers must undergo quality testing before use.
Explanation: Quality tests include load-bearing capacity, dimensional accuracy, water permeability, and chloride diffusion resistance, in compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN.
Optimization: Ensure the product is certified by reputable organizations like ISO or ASTM
Answer: Yes, if the concrete spacers are designed to meet the required load standards.
Explanation: Fiber-reinforced or high-strength concrete spacers with a compressive strength above 60 MPa are suitable for heavy load structures like bridges or foundations.
Optimization: Use spacers tested for a breaking load of over 6 kN to ensure safety
Answer: Yes, concrete spacers have better heat resistance compared to plastic spacers.
Explanation: Concrete spacers do not deform or lose quality at high temperatures, making them ideal for industrial furnaces or fire-resistant structures.
Optimization: Choose special concrete spacers for extreme temperature conditions
Answer: No, as long as they are manufactured to standard specifications.
Explanation: Concrete spacers are designed to withstand environmental conditions and become a permanent part of the structure.
Optimization: Store in a dry area before use to prevent damage or quality degradation
Answer: Yes, concrete spacers help ensure the concrete cover thickness meets requirements, reducing the risk of corrosion.
Explanation: Proper spacers maintain the concrete cover, minimizing water or chloride penetration, thereby lowering corrosion risk.
Optimization: Use high-quality spacers in structures exposed to severe corrosion, such as coastal areas.
Answer: Yes, it is essential to ensure even distribution and correct positioning.
Explanation: Incorrect placement can imbalance the reinforcement and reduce the protective efficiency of the concrete cover.
Optimization: Use detailed technical drawings to precisely position each spacer
Answer: Single-size spacers provide one specific cover thickness, while multi-size spacers can be used for various cover thicknesses.
Explanation: Multi-size spacers offer greater flexibility, reducing the number of spacers needed and optimizing costs.
Optimization: Use multi-size spacers for projects requiring multiple cover thicknesses
Answer: Concrete spacers maintain a minimum 50 mm cover in foundations, ensuring reinforcement is protected from soil or groundwater corrosion.
Explanation: The thicker concrete cover in foundations resists high moisture levels and corrosive substances in the soil.
Optimization: Choose high-load-bearing concrete spacers for large foundation systems.
Answer: Optimize design, select multi-size spacers, and ensure quality control during construction.
Explanation: Proper spacer selection and efficient distribution reduce waste and costs while maintaining quality.
Optimization: Partner with reputable manufacturers to purchase spacers in bulk
Answer: They can be, but attention must be paid to the load-bearing capacity of the spacers, especially with dense reinforcement.
Explanation: Lightweight concrete typically has lower strength, so spacers must provide sufficient load capacity to compensate.
Optimization: Use high-strength or fiber-reinforced concrete spacers for such projects




















